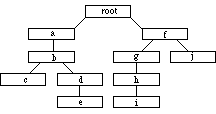
Example for structure of file format. This tree is written in preorder as: (root(ab(c)(de))(f(ghi)(j)))
![[SGF FF[4] - Smart Game Format]](../images/head.png)
Copyright Anders Kierulf, 1990
A standard file format to exchange machine-readable games, problems, and opening libraries would save time and work. That goal may not be too far away. A standard for exchanging collections of Othello games is being worked out by Erik Jensen, Emmanuel Lazard, and Brian Rose in collaboration with the author. For Go, a new standard has recently been proposed [Connelley 89, High 89]; it seems to suffer from a wealth of features, but any standard for exchanging Go games is welcome, and will be supported by the Smart Game Board.
The current file format is specialized for the needs of the Smart Game Board. It is based on an earlier proposal for a standard for Go games [Kierulf 87b] which was not widely adopted. The following description is not a new proposal; it is intended for those who want to read or write files that are compatible with the Smart Game Board.
The game collections (documents) of the Smart Game Board are stored as text files. This has the advantage that files can be manipulated with standard text utilities, and that it's easier to exchange games by electronic mail. The disadvantage is that text files are less compact than binary files.
The Smart Game Board stores the game trees of each document, with all their nodes and properties, and nothing more. Thus the file format reflects the regular internal structure of a tree of property lists. There are no exceptions; if a game needs to store some information on file with the document, a (game-specific) property must be defined for that purpose.
I will first define the syntax of the game collections, then discuss syntax and
semantic of various properties.

Example for structure of file format.
This tree is written in preorder as:
(root(ab(c)(de))(f(ghi)(j)))
Thus the main branch of the game is stored first in the file, and programs can easily read that part (until the first closing parenthesis) and ignore the rest.
The conventions of EBNF are discussed in [Wirth 85]. A quick summary:
"..." : terminal symbols
[...] : option: occurs at most once
{...} : repetition: any number of times, including zero
(...) : grouping
| : exclusive or
The overall definition of the file format is as follows:
Collection = {GameTree}.
GameTree = "(" Sequence {GameTree} ")".
Sequence = Node {Node}.
Node = ";" {Property}.
Any text before the first opening parenthesis is reserved for future extensions and is ignored when reading a file. Spaces, tabs, line breaks and so on can be inserted anywhere between properties and are also ignored.
Property = PropIdent PropValue {PropValue}.
PropIdent = UpperCase [UpperCase | Digit].
PropValue = "[" [Number | Text | Real |
Triple | Color | Move | Point | ...] "]".
Number = ["+"|"-"] Digit {Digit}.
Text = { any character; "\]" = "]", "\\" = "\"}.
Real = Number ["." {Digit}].
Triple = ("1" | "2").
Color = ("B" | "W").
Move and Point are game-specific and are described later. The following properties are understood by all games. The property type is given in brackets.
"B" : Black move [move, game-specific]
"W" : White move [move, game-specific]
"C" : comment [text]
"N" : node name [text]
The purpose of providing both a node name and a comment is to have a short identifier like "doesn't work" or "Dia. 15" that can be displayed directly with the properties of the node, even if the comment is turned off or shown in a separate window. There is no limit to the length of texts; programs must be able to ignore the rest of texts that are too long for them to handle. Reasonable limits are 32 characters for node names and at least 2000 characters for comments.
"V" : Node value [number]
Positive values are good for Black, negative values are good for White. The interpretation of particular values is game-specific.
"CH": check mark [triple]
"GB": good for Black [triple]
"GW": good for White [triple]
"TE": good move (tesuji) [triple]
"BM": bad move [triple]
The normal value for such properties is one, properties that are doubled for emphasis have the value two.
"BL": time left for Black [real]
"WL": time left for White [real]
All times are given in seconds, or fractions thereof.
"FG": figure [none]
The figure property is used to divide a game into different figures for printing: a new figure starts at the node with a figure property.
"AB": add black stones [point list, game-specific]
"AW": add white stones [point list, game-specific]
"AE": add empty = remove stones [point list, game-specific]
"PL": player to play first [color]
The above properties are used to set up positions in games with only black and white stones. The following properties are all part of the game info:
"GN": game name [text]
"GC": game comment [text]
"EV": event (tournament) [text]
"RO": round [text]
"DT": date [text]
"PC": place [text]
"PB": Black player name [text]
"PW": White player name [text]
"RE": result, outcome [text]
"US": user (who entered the game) [text]
"TM": time limit per player [text]
"SO": source (book, journal, ...) [text]
The format in these game-info strings is free, but to be able to search for specific games in game collections, it is recommended to adhere to the following conventions:
The following properties may only be present at the root node:
"GM": game [number] (Go=1, Othello=2, chess=3, Nine Men's M.=5)
"SZ": board size [number]
"VW": partial view [point list, game-specific]
"BS": black species [number] (human=0, modem=-1, computer>0)
"WS": white species [number]
The game number helps the program reject games it cannot handle (this property was mandatory as long as an application could play different games). The view gives two corner points of a rectangular subsection; an empty list denotes the whole board. The species denotes the kind of player (the source of the move input), with different versions of computer algorithms denoted by positive numbers (default algorithm = 1).
Computer algorithms may add the following properties:
"EL": evaluation of computer move [number]
"EX": expected next move [move, game-specific]
Some games support markings on the board: selected points, triangles/crosses, or letters (a sequence of letters is shown on the points given in the list, starting with "A"):
"SL": selected points [point list, game-specific]
"M" : marked points [point list, game-specific]
"L" : letters on points [point list, game-specific]
Remark by Martin Müller: this has been superseded by the new "LB" label
property
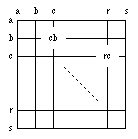
Coordinate system used to write Go games to disk
The first letter designates the column (left to right), the second the row (top to bottom). The upper left part of the board is used for smaller boards, e.g. letters "a"-"m" for 13*13. (Column before row follows the principle "horizontal before vertical" used in x-y coordinate systems. The upper left corner as origin of the board corresponds to the way we read, and most modern computers use it as origin of the screen coordinates to simplify integration of text and graphics.) A pass move is written as "tt". The board must be quadratic, no smaller than 2*2, and no larger than 19*19. Additional game info properties are defined for Go: "BR": Black's rank [text]
"WR": White's rank [text]
"HA": handicap [number]
"KM": komi [real]
Sets of board points can be marked as territory, as secure stones, or just as a region of the board (e.g. to designate eye space):
"TB": Black territory [point list]
"TW": White territory [point list]
"SC": secure stones [point list]
"RG": region of the board [point list]
"PE": perfect score [number]
"OS": optimal score [number]
"OE": number of empty for optimal score [number]
Martin Müller, mueller@inf.ethz.ch